The National Aeronautics and Space Administration has been at the forefront of climate science, launching satellites that take the pulse of Earth’s land, oceans and atmospheric systems, gathering data on climate, weather and natural hazards. But the agency is increasingly vulnerable itself to the effects of a changing climate.
Tag Archives: NASA-GISS
The New Climate Dice: The Odds Have Shifted to Hot
First posted on the Earth Institute’s State of the Planet blog on Aug. 6, 2012
This year’s Midwest heat wave and some other recent extreme weather events are no fluke of nature, but a consequence of a warming planet, according to an analysis of climate data by NASA scientists. The odds of an unusually hot summer have doubled since mid-century, according to the research by NASA’s James Hansen and two colleagues, published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
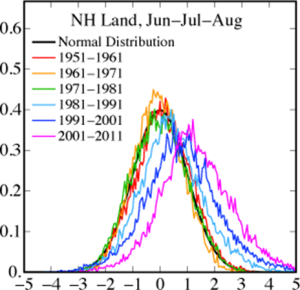
Furthermore, the researchers found that the extremes of heat are getting even hotter, creating in essence a new “normal” for climate. On average, 10 percent of land area across the planet now experiences these more extreme temperatures, a more than tenfold increase from 1951 to 1980, when less than 1 percent of global land area reached this extreme.
“This summer people are seeing extreme heat and agricultural impacts,” Hansen said. “We’re asserting that this is causally connected to global warming, and we present the scientific evidence for that.”
Hansen and colleagues analyzed mean seasonal temperature in June, July and August during the last 30 years and showed that the odds have increased for an anomalously hot summer – a period of average temperatures that reach more than 0.43 standard deviations from the norm. Specifically, 75 percent of global temperature anomalies now fall into the hot category, compared to just 33 percent from 1951 to 1980.
Hansen has used the “climate dice” analogy to explain this: In the 1980s, he looked at the summers between 1951 and 1980; he put the 10 hottest into one category, the 10 coldest into another, and the 10 falling in between into a third. These, he said, could be characterized by the six sides on dice: Two sides red for hot summers, two sides blue for cool, and two sides white for “normal.” For the period there was an equal chance of any of the three occurring.
Compared to that 30-year period, the dice now are loaded for hot summers: Four sides red, one blue and one white.
U.S., 5 Nations to Cut Methane, Soot Emissions
This was first posted on the Earth Institute’s State of the Planet blog on Feb. 17, 2012

Redesigning cookstoves is one of the ways to cut emissions of black carbon soot. For a slide show from NASA showing 14 ways to curb emissions that add to global warming and harm human health, click on the photo. (Photo: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center)
The United States and five other countries agreed this week to fund an effort to cut emissions of methane, soot and other pollutants to start to slow the rate of human-induced climate change.
The effort, for which the nations pledged $27 million, will use existing technologies such as improved cook stoves and capturing methane from landfills in an effort scientists say could slow global mean warming 0.5 degrees C by 2050.
The other countries who have pledged to join the fight include Canada, Mexico, Bangladesh, Sweden and Ghana.
The program was spurred in part by a recent paper in Science co-authored by Drew Shindell of NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies, affiliated with the Earth Institute, and a June 2011 report from the UN Environment Programme, chaired by Shindell, and the World Meteorological Organization. (A recent story about the report appears on the Earth Institute web site, and a related piece on the State of the Planet blog.) Continue reading →
Filed under Climate, Environment, Stories
Tagged as black carbon soot, climate change, emissions, methane, NASA-GISS, soot